Queue (data structure) implementation using singly linked list in Python
Today I’ll talk about how to implement Queue data structure using another data structure Singly linked list in Python. If you want to know how to implement Singly linked list in Python then read this previous blog post Singly linked list.
First, let’s know about Queue data structure. Queue is a particular kind of abstract type data structure, it is a FIFO (First in First out) data structure. In a FIFO data structure , an item inserted in first , will be removed first. Inserting an element in Queue is called enqueue and removing an element from it is called dequeue.
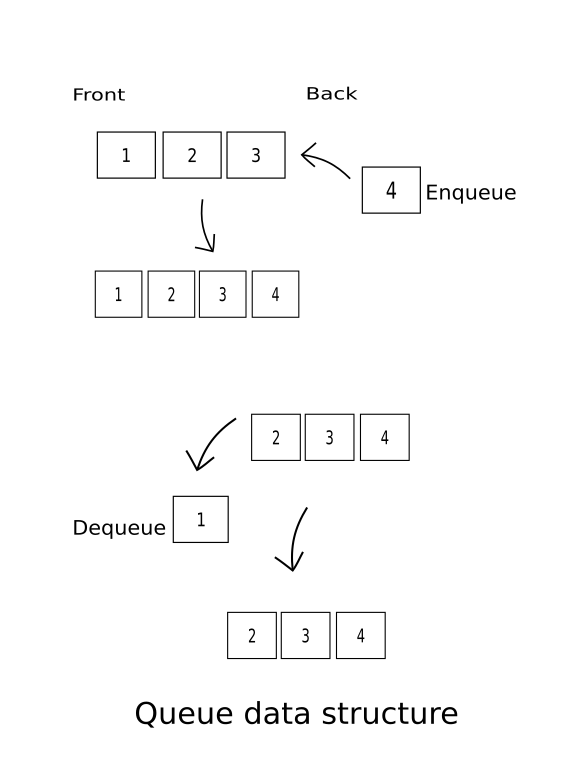
Here I’ll show you how to enqueue , dequeue and in addition - how to get the size of queue , check if queue is empty or not, and at last how to print it as a list/array.
So , let’s start coding.
I’m gonna use Singly linked list to implement Queue data structure, so according to linked list first create a Node class , by which we can create an element with a given data to be enqueued in Queue.
In the Node class, we will set the data and next_node(i.e pointer) equal to None as parameter in init method so that if we don’t send any data and pointer to the next node, it will return None. Then get_data and get_next methods will return the data and the next node respectively. We will add another method set_next which will take a new_node as a parameter and will set the pointer from previous Node towards this Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self,data=None,next_node=None):
self.data = data
self.next_node = next_node
def get_data(self):
return self.data
def get_next(self):
return self.next_node
def set_next(self,new_node):
self.next_node = new_node
After that create another class named Queue, and set the head (1st element of Queue) = None as parameter in init method. Then we will insert an element at first of Queue using enqueue method. The enqueue method takes a data as parameter and create a Node using it. Now, we’ll check if there is any head in Queue! If it hasn’t one,we set the Node(new_item)/element created previously as head. If there is already a head i.e. there are elements in Queue. So, we will go to the end of Queue using while loop and when we find that pointer of the previous node is null, we set the pointer of last Node/element towards the Node we created.
class Queue:
def __init__(self,head=None):
self.head = head
def enqueue(self,data):
new_item = Node(data)
current = self.head
if current is None:
self.head = new_item
else:
while current.get_next():
current = current.get_next()
current.set_next(new_item)
Now it’s time to add a method dequeue to remove the first element from the Queue. First, we check whether the Queue is empty or not , if it is not empty then we set the second element of Queue as head and first element(self.head) which was initially stored in current get removed. Again, if the Queue is empty, we simply print “Queue is empty.” .
def dequeue(self):
current = self.head
if current != None:
self.head = current.get_next()
else:
print("Queue is empty.")
Using dunder method len, so that we can get the size of Queue using len() over the Queue we have written.
def __len__(self):
return len(self.temp)
Let’s create another method is_empty which tells us whether the Queue is empty or not! If self.head(1st element of Queue) is None i.e. there is no element it returns False , else returns True.
def is_empty(self):
if self.head == None
It’ll be better if can visualize the Queue as a list/array. So, this print_queue method gets the job done. First, just set the head/1st element to current variable and create an empty list which we can store in a variable , let’s name it temp. Now, we go through the whole Queue using while loop and every time we find an element ,just append it to temp list and go to next element. At the end print temp.
def print_queue(self):
current = self.head
self.temp = []
while current:
self.temp.append(current.get_data())
current = current.get_next()
print(self.temp)
Okay,you see that we have implemented a Queue using Singly linked list in Python. It’s checking time whether the code works as expected.
q = Queue()
q.enqueue("User01")
q.enqueue("User02")
q.enqueue("User03")
q.enqueue("User04")
q.enqueue("User05")
q.print_queue()
>>> ['User01', 'User02', 'User03', 'User04', 'User05']
q.dequeue()
q.print_queue()
>>> ['User02', 'User03', 'User04', 'User05']
q.dequeue()
q.print_queue()
>>> ['User03', 'User04', 'User05']
print(len(q))
>>> 3
print(q.is_empty())
>>> False
That’s how you can implement a Queue data structure using Singly linked list in Python. Hope , my explanation helps the guys out there who are learning data structure using Python. Keep learning!